Get to know Spectrum Academy
An educational portal addressed to specialists interested in the use of medical cannabis.
Spectrum Academy - medical cannabis in practice | Cannabinoids and their role in medicine

Medical cannabis – introduction
More than 500 natural chemical compounds have been identified and isolated in Cannabis sativa L.. They include medically important cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids and other ingredients.
These ingredients are present in high concentrations in secretory hairs, i.e. hair-like structures that secrete glandular resin. These glands are located on the surface of the flowers of female cannabis plants.
Hemp
Over 500 natural chemical compounds have been identified and isolated in Cannabis sativa. These are medically important cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids and other non-cannabinoid ingredients.
These ingredients are produced in high concentrations in trichomes, which are hair-like, resin-secreting glands found on the surface of female cannabis flowers.
Cannabinboids
Research lists over 100 cannabinoids that interact with cannabinoid receptors in the body:
- endocannabinoids – produced naturally in the body
- phytocannabinoids – found in many plants, but in the highest concentration in hemp
- synthetic cannabinoids – pharmaceuticals that are analogues of THC (e.g. nabilone) or mixtures of THC and CBD extracted from plants (e.g. nabiximols)

Cannabinoid activation
The inactive delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) contained in the unprocessed plant must be decarboxylated into neutral phenols (THC and CBD) in order to interact with the endocannabinoid system. This occurs when dried cannabis flowers are heated, such as by vaporizing, smoking, baking or cooking. Many commercially available oils are decarboxylated to enable consistent, precise dosing.
Terpenes and flavonoids
They are responsible for the variety of smells and flavors of different cannabis varieties. Terpenes may have a direct physiological effect and may also interact with cannabinoids, giving particular properties to particular varieties of cannabis.
This is the so-called "Entourage Effect", a theory that describes possible interactions between primary cannabinoids, secondary cannabinoids, terpenes and other components of the plant.
The endocannabinoid system
The endocannabinoid system is a ubiquitous lipid signaling system that plays an important role in regulating homeostasis throughout the human body.
Has an influence on:
- development of the nervous system
- immune functions
- inflammations
- appetite
- metabolism and regulation of energy management
- functioning of the circulatory system
- digestion
- development of the skeletal system and regulation of bone density
- synaptic plasticity and learning processes
- pain, reproduction
- mental disorders
- psychomotor behaviors
- memory
- sleep and wake cycles
- regulation of stress and emotional state
Receptors
The endocannabinoid system consists of CB1 and CB2 receptors, two endogenous agonists (endocannabinoids) and enzymes that regulate the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. The concentration of CB1 receptors is greatest in the central and peripheral nervous system and in the gastrointestinal tract. CB2 receptors are found mainly in the immune system, including the tonsils, spleen, lymph nodes, and lymphocytes and neutrophils in the peripheral blood.
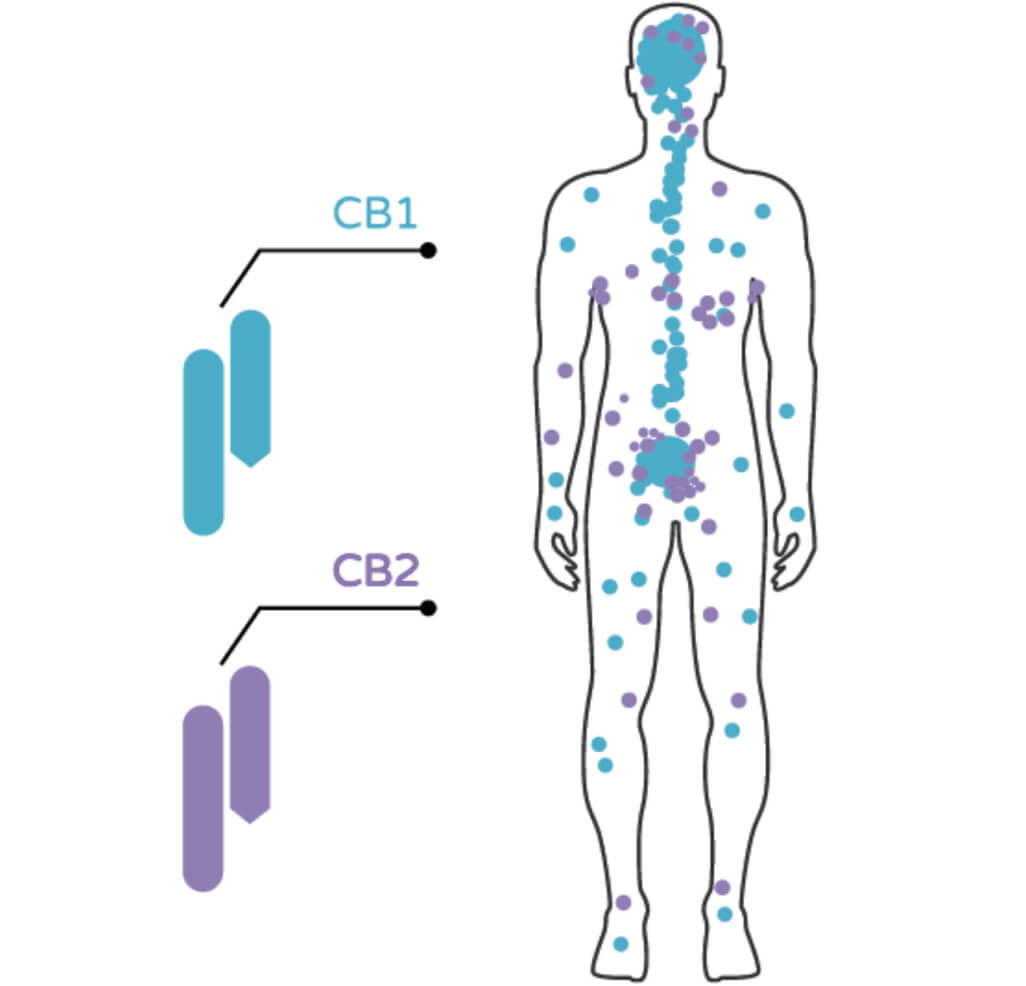
Although they are present throughout the central nervous system, the concentration of cannabinoid receptors is low in the brainstem, especially in the area responsible for the regulation of cardiorespiratory activity. Therefore, unlike opioids, it is almost impossible to induce cardiorespiratory collapse and death with cannabinoids.
Activation of CB1 receptors
This neuronal connection diagram shows the activation of CB1 receptors by endocannabinoids. This retrograde signaling regulates neurotransmission in a temporally and spatially precise manner.
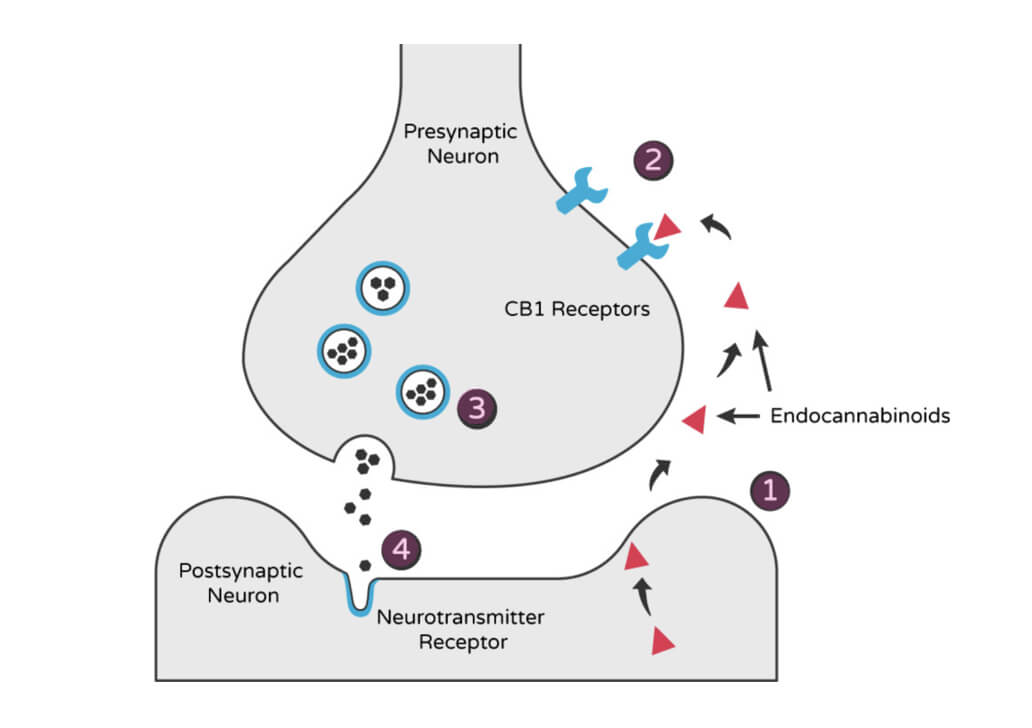
- Endocannabinoids are produced in the postsynaptic terminal in response to cellular demand.
- These ligands pass through the synaptic cleft and bind to cannabinoid receptors (i.e. CB1) on the cell surface of the presynaptic terminal.
- When stimulated, cannabinoid receptors activate a signaling cascade that suppresses the release of neurotransmitters (i.e. glutamate, GABA, dopamine and cholecystokinin) into the synaptic cleft.
- Suppression of neurotransmitters changes the frequency of action potential generation in postsynaptic neurons.
Methods of Administration
Ingestion by mouth
Consuming cannabis orally via a dropper or in softgel form ensures dosage accuracy. It is not recommended to add hemp oil to bread or other food (e.g. yogurt), as this results in a loss of dosage precision.
Inhalation
Vaporization
Vaporization is a method that enables the inhalation of biologically active components of medical cannabis without burning the plant material. This process involves heating the cannabis to a temperature that causes the cannabinoids and other essential components of the plant to release, without combustion occurring. This reduces the amount of toxic by-products generated during smoking. The vaporization method limits the damage associated with smoke inhalation, while being a much more effective method of extracting chemically active ingredients. This also reduces cannabinoid losses in lateral smoke, leading to significant cost savings compared to traditional smoking.
Smoking
Smoking is the most common but not recommended method of consuming cannabis. Smoking plant substances is associated with serious adverse health effects. Smoking releases toxins and toxic substances such as ammonia, carbon monoxide, tar and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Our products
We offer a diverse range of dried flower products. Healthcare professionals and patients can use our easy-to-use color code to easily identify the right products that meet their treatment needs.




